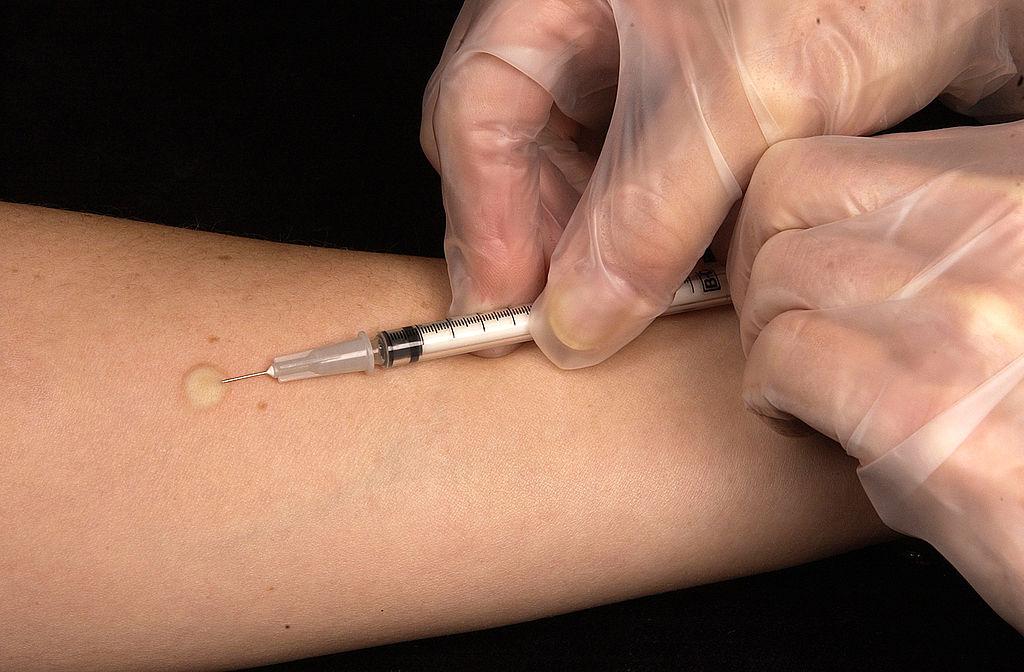
Injection into the dermal skin layer | Intradermal vaccination
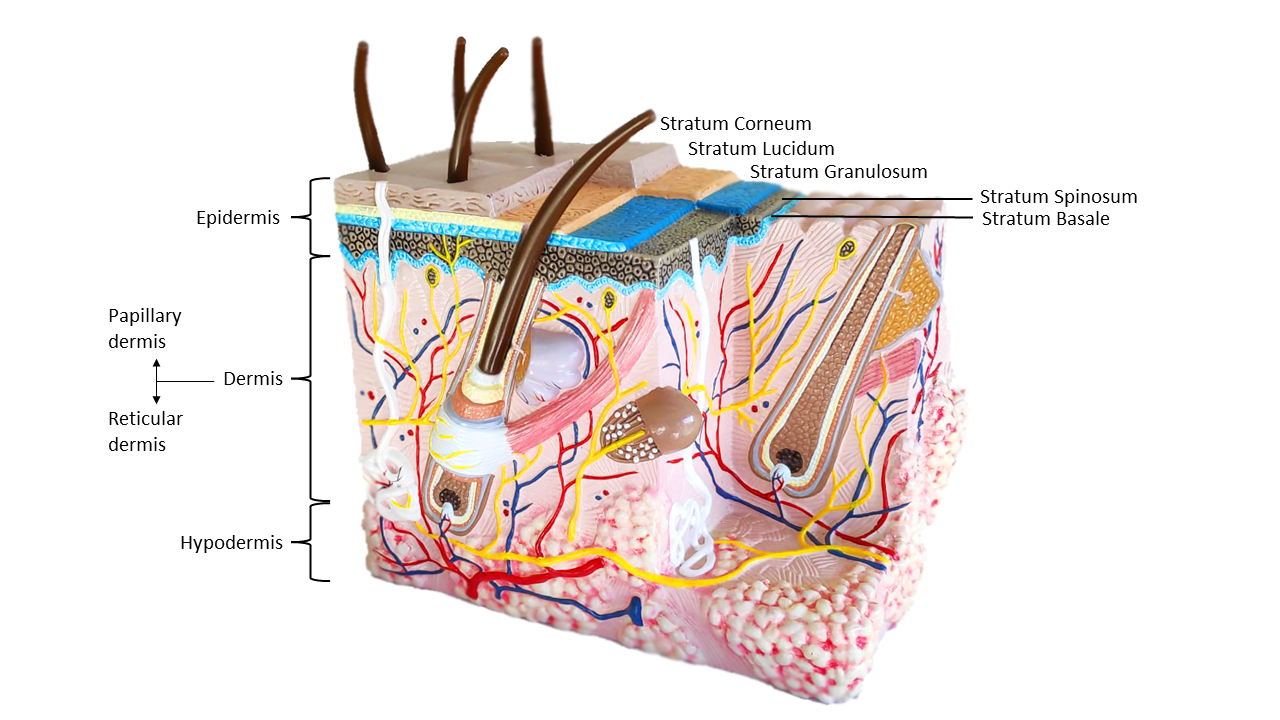
Vaccines can be administered via the intradermal route, i.e. injection in the dermis, one of the layers of the skin (cfr picture). This layer, underneath the epidermis, is highly vascularized and contains a large amount of immune cells, mainly dermal dendritic cells.
Vaccination through intradermal injection holds many advantages compared to other types of vaccination, such as an improved immune response to vaccine, a potential reduction of the antigen dose (9), and decreased anxiety and pain (1-3;5;6).
The VAX-ID® device is suited for reliable and easy intradermal injections and vaccination. The short intradermal needle, protected by a plastic holder, causes less pain in patients and prevents needle-stick injuries. Read the VAX-ID® product specification page to learn more about the device.
Definition of intradermal injection
Intradermal injection is one of the routes of administration used for vaccination. The three main routes are intradermal (ID) injection, subcutaneous (SC) injection and intramuscular (IM) injection. Each type targets a different skin layer:
- Subcutaneous injections are administered in the fat layer, underneath the skin.
- Intramuscular injections are delivered into the muscle.
- Intradermal injections are delivered into the dermis, or the skin layer underneath the epidermis (which is the upper skin layer). The dermis is, on most places of the human body, only a few mm thick.
Intradermal injection methods
Intradermal injections can be delivered using either normal-sized needles using the Mantoux technique or specifically designed devices.
With a normal-sized needle: Mantoux technique for intradermal injection
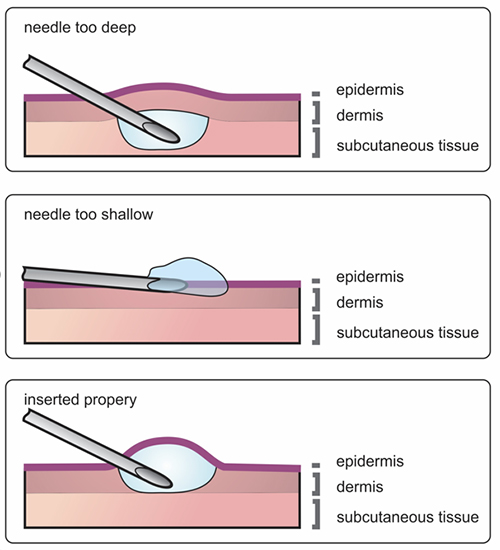
The currently used Mantoux technique (see picture) requires a high amount of training. It is difficult to standardize as it uses a regular needle and syringe to be inserted at an angle of 10 to 15° bevel up. Injecting the needle too deep will lead to leakage to the subcutaneous layer (fat layer), while injecting the needle too shallow will cause leakage to the outside of the skin. It has been shown that about 70% of intradermal injections using the Mantoux technique are incorrectly administered (Micheels & Goodman, 2018). For that reason, intradermal injection is at present not often used for vaccination, even though intradermal vaccination holds many advantages over other types of vaccination. (1-5)
An alternative method for the Mantoux technique is intradermal microinjection. Certain micoinjection devices, such as VAX-ID®, offer a solution to the problem of the Mantoux technique.
Using shorter needles
Intradermal microinjection
The dermis is located right underneath the epidermis, or the upper skin layer. Therefore, it can easily be reached by a shorter needle, if that needle is placed at a 90-degree angle.
In other words, the dermis can be easily reached by intradermal microinjection. Intradermal microinjection involves injection systems especially designed for intradermal injection with mini-needles, such as the VAX-ID®. The advantage of such systems is their usability, allowing the tool to be used also by untrained staff (1;3;6). They also evoke less pain for the patient, and the shortness of the injection needle makes injections safer (1-3;5;6).
Microneedle arrays for intradermal injection
New intradermal injection devices are in development, including microneedle arrays.
Microneedle arrays consist of multiple microneedles, which can be solid or biodegradable (dissolving in the body after injection). A difference can be made between solid intradermal microneedles made from a non-degradable material, such as stainless steel, glass, or titanium; and solid microneedles with hollow centers. Sometimes intradermal microneedles are combined with an adhesive patch. (1;6)
Self-dissolving microneedles can be made of sugar, sugar derivatives, or other self-dissolving materials. The advantage of this type of intradermal vaccination is the lack of sharp waste, as the needles dissolve within minutes after vaccination. (1;6)
Most of these intradermal needle arrays, however, are currently only available for research or investigational purposes.
Tattoo devices for intradermal injection
Tattoo devices can be used for vaccination: with this technique a short injection needle (or multiple needles) penetrates the skin through vibrations at a high frequency. The main advantage of this intradermal injection method is the large surface area the vaccine is injected in, which causes it to affect a broader cell population. (1;6)
This technique, however, is currently only available for research.
Needle-free
Intradermal liquid jet injectors
Jet injectors are needle-free and use a high pressured, fast stream of injection liquid (or vaccine) to penetrate the skin (6). sometimes small amounts of vaccine do not enter the skin, but “splash back” from the device, often alarming both patient and administrator (1).
Intradermal jet injectors have been used in mass vaccination projects and in low and middle income countries, or as an alternative for insulin injection for diabetic patients.
Ballistic intradermal injectors
Other than intradermal jet injectors, ballistic injectors do not send out a liquid stream to penetrate the skin, but solid particles. Multiple versions of this intradermal injection method exist, but most of them are only available for research. Examples include the “gene gun” for transferring genes, and devices which penetrate the skin with gold or sugar particles. (1;6)
Sources:
- Kis EE, et al. Vaccine. 2012. PMID:22100637
- Kim YC, et al. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2012. PMID:21472533
- Young F, Marra F. Vaccine. 2011. PMID:21968444
- Combadiere B, Liard C. Human Vaccines. 2011. PMID:21817854
- Lambert PH, Laurent PE. Vaccine. 2008. PMID:18486285
- WHO, PATH. 2009. PDF site WHO
- Wang PM, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2006. PMID:16484988
- Mitragotri S. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005. PMID:16239901
- Zehrung D, et al. Vaccine. 2013. PMID:23176978
Interested in our solutions?
Contact our commercial team!
