Aim
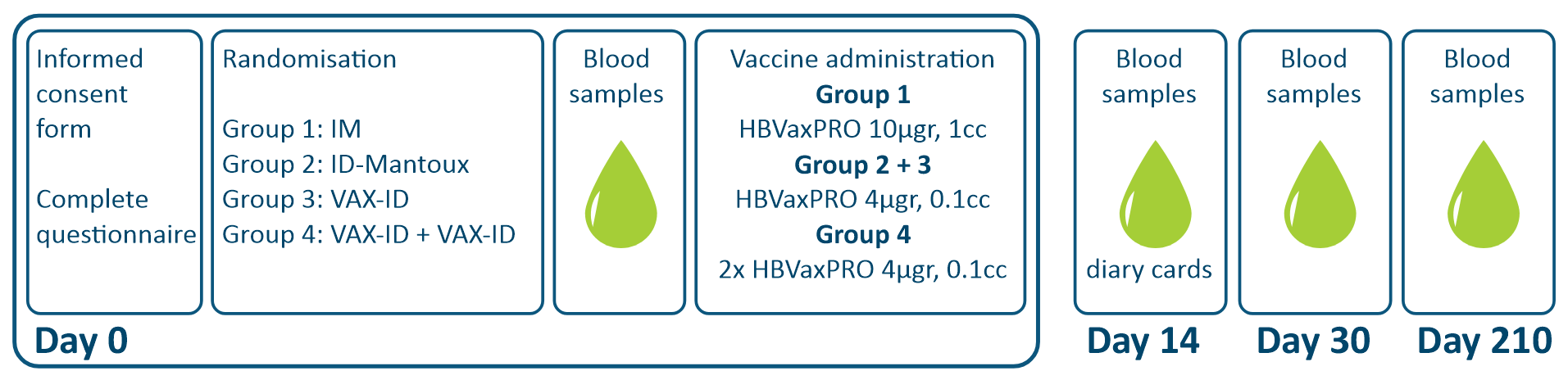
Immunogenicity and safety of VAX-ID was assessed in a non-inferiority study using a Hepatitis B vaccine.
Methods
Van Mulder et al. investigated the immunogenicity and safety of intradermal delivery of a hepatitis B booster vaccine using this novel drug delivery device, VAX-ID®.
A total of 48 healthy adults were enrolled for the study and divided over 4 groups: (1) standard Intramuscular (IM) injection in the deltoid region (HBVAXPRO® 10 µg, 1 mL), (2) Intradermal (ID) injection in the proximal posterior area of the forearm using the Mantoux technique, (3) ID injection with VAX-ID® in one forearm, or (4) ID injection with VAX-ID® in both forearms. The ID groups received a fractional dose of the HBVAXPRO (1/4th, HBVAXPRO 4µg, 0.1mL) compared to full dose in the intramuscular group.
Results
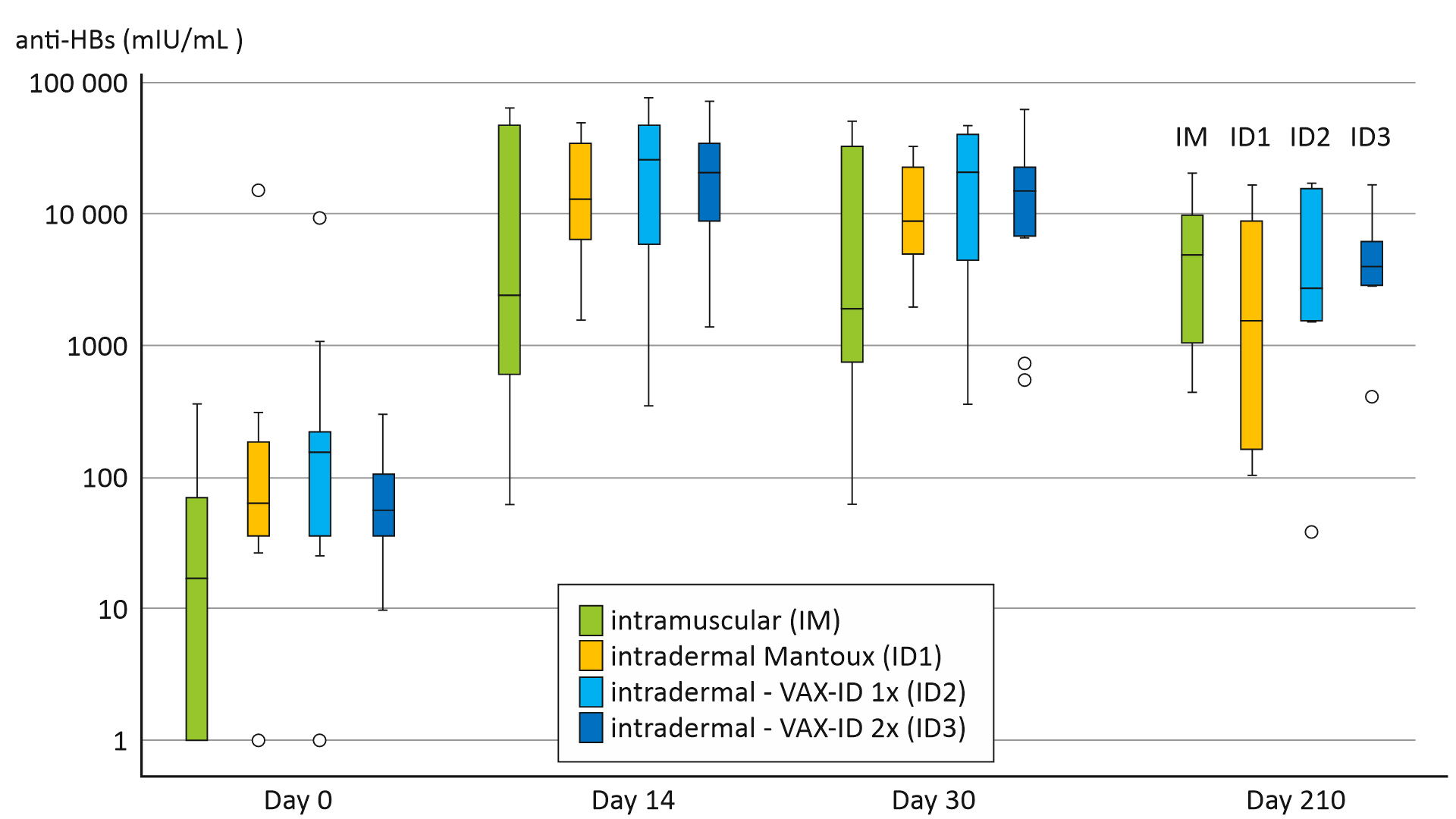
The results of the study demonstrated promising immunogenicity of the intradermal Hepatitis B booster vaccine using VAX-ID®. Importantly, the vaccine delivered through the intradermal route produced robust antibody responses. This indicates its ability to stimulate the immune system effectively. Indeed, the immunogenicity of the intradermal vaccine was non-inferior to the standard intramuscular vaccination.
Furthermore, the study reported a favourable safety profile for the intradermal delivery method. Also, the incidence of local and systemic adverse reactions was minimal and comparable to those observed with the Mantoux.
Conclusion
The findings of this study highlight the potential of the intradermal route using VAX-ID® as a viable option for Hepatitis B vaccination.
Interested in our solutions?
Contact our commercial team!
